Automatic Cancer Staging through AI-driven Image Analysis
ARCADIA is a groundbreaking research initiative developed in collaboration with CRS4, Sardinia’s leading research center. It introduces a sophisticated system designed to support doctors in the accurate diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Utilizing 3D ultrasound scans, ARCADIA automates tumor segmentation, stage classification, and identifies infiltrated lymph nodes.
Introduction
The automatic staging of colorectal cancer using artificial intelligence represents a crucial advancement in medical diagnostics today. Leveraging supervised and semi-supervised learning techniques alongside deep learning in computer vision, ARCADIA transforms ultrasound outputs into automated diagnoses.
The project
Our approach centers on empowering the model to initially assess key metrics and parameters. Doctors can then review and refine these assessments as needed, enhancing report accuracy. Validated data is stored in a data lake, continuously improving model quality through iterative retraining. This synergy optimizes clinical workflows, offering expedited diagnosis and treatment planning.
The structure
On Top: On-premises computing using models from the DL-CRT library, employing Python for compute-intensive tasks with CPU and GPU support.
On Centre: Cloud-based aggregation of CRT datasets, utilizing TPU and GPU for high-performance DL modeling, ensuring model optimization and scalability.
On Bottom: A collaborative data lake sourced globally, standardizing image metadata and annotations for DL model training.
Image Segmentation
Prior to deployment, rigorous training is essential. Developing a robust segmentation system involves overcoming challenges like limited labeled data. Our solution includes a semi-supervised model capable of learning from partially annotated datasets, streamlining the segmentation of 2D and 3D images crucial for accurate diagnostics.
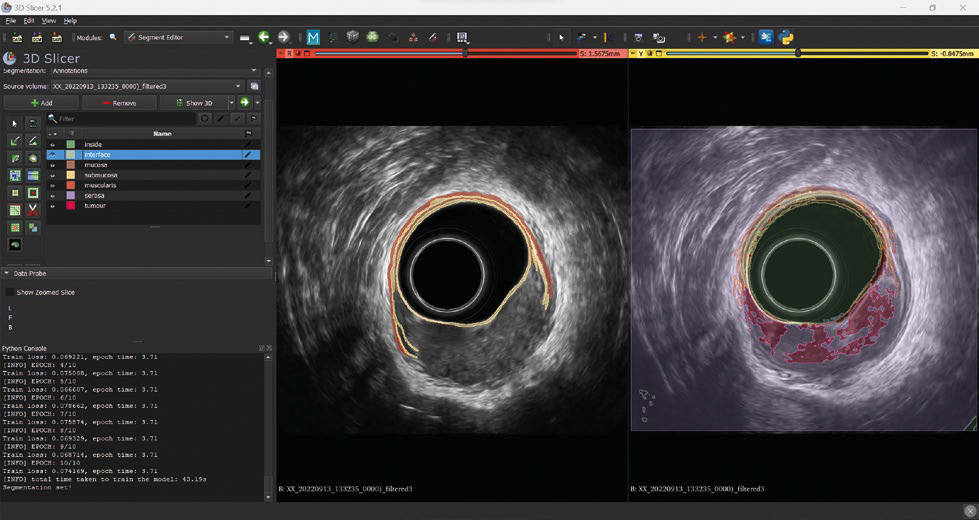
On the left of the image, a partial annotation on a single slice, where just the classes “interface”, “mucosa”, “submucosa” and “muscularis” are annotated. On the right, the segmentation suggested by the model during the training phase
Semi-supervised Learning
By training with partially labeled data, our approach maximizes efficiency while minimizing costs associated with manual annotation. This method enhances model accuracy by iteratively refining segmentation through expert validation.
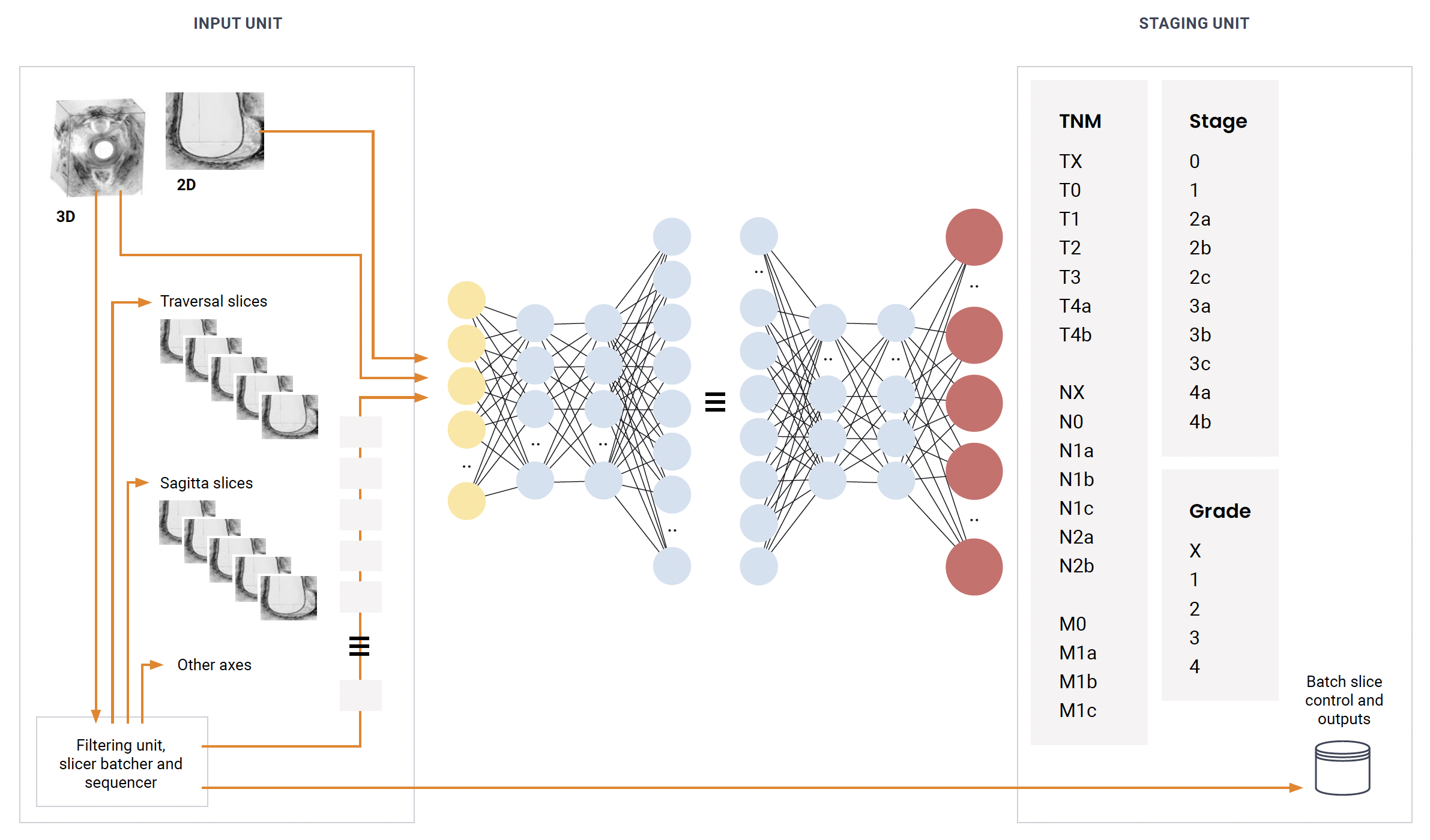
The Model
The core of our system is a Unet model, a CNN architecture adept at image segmentation tasks. Trained initially on fully labeled images and supplemented with partially labeled data, it extracts and refines features critical for precise tumor identification and staging. The model’s scalability allows it to extend from 2D to comprehensive 3D volume analysis, culminating in detailed segmentation maps essential for clinical decision-making.
